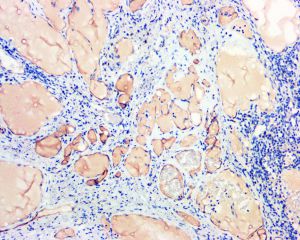
淋巴管瘤
Lymphangioma
夏成青 赵明 刘正智
发布时间:2016-08-02 14:46:05
概述:
发病部位:好发于头颈部、腋窝,偶见肺、胃肠道、肝、骨等。
诊断要点:
1.常见于儿童(出生时或2岁以内),典型表现为大的、缓慢生长的、无痛性肿块,多个浅表的水泡样病变;好发于头颈部、腋窝,偶见肺、胃肠道、肝、骨、脾等;
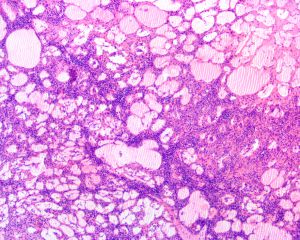
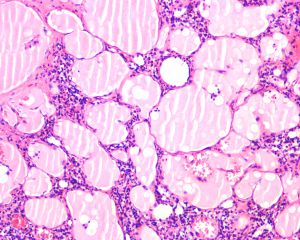
2.呈单房或多房性,囊壁薄,囊内充满清亮的液体;
3.通常分为4种类型:海绵状淋巴管瘤、囊性淋巴管瘤、局限性淋巴管瘤和获得性进行性淋巴管瘤;
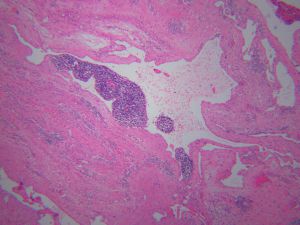
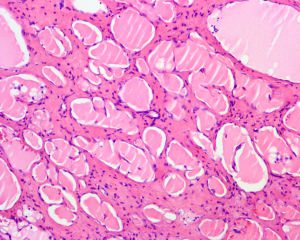
4..镜下由大小不等的腔隙组成,腔内壁衬以单层的扁平内皮细胞,腔内充满蛋白性液体,常可见淋巴细胞,有时可见红细胞;
5.在大的腔隙周围常可见不完整的平滑肌。
免疫组织化学染色:
分子标记:
鉴别诊断:
1、血管瘤:大多数病例血管较小,红细胞较多,蛋白质物质较少,淋巴细胞较少。
2、渐进性淋巴管瘤:典型表现为成人下肢生长缓慢的斑块,表面扩张的管腔随着深度的扩展而逐渐变小。
3、继发性淋巴管扩张症:可能是由于局部因素,如梗阻、瘢痕形成或放射治疗。
预后:
治疗:
参考文献:
1.Blei F: Lymphangiomatosis: clinical overview. Lymphat Res Biol. 9(4):185-90, 2011
2.Gupta SS et al: Cystic lymphangioma of the breast in an 8-year-old boy: report of a case with a review of the literature. Surg Today. 41(9):1314-8, 2011
3.Xu GP et al: Splenic cystic lymphangioma in a young woman: case report and literature review. Acta Gastroenterol Belg. 74(2):334-6, 2011
4.Ji RC et al: Multiple expressions of lymphatic markers and morphological evolution of newly formed lymphatics in lymphangioma and lymph node lymphangiogenesis. Microvasc Res. Epub ahead of print, 2010
5.Kim DH et al: Lymphangiomatosis involving the inferior vena cava, heart, pulmonary artery and pelvic cavity. Korean J Radiol. 11(1):115-8, 2010